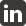Sandbag Structures by Nader Khalili
The global need for housing is felt by millions refugees and displaced persons – victims of natural disasters and wars. Iranian architect Nader Khalili believes that this need can be addressed only by using the potential of earth construction.
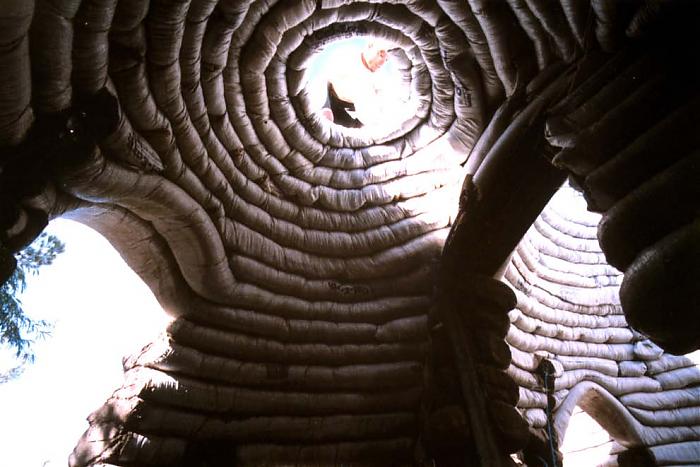
After extensive research into vernacular earth building methods in Iran, followed by detailed prototyping, he has developed the sandbag or ‘superadobe’ system. The basic construction technique involves filling sandbags with earth and laying them in courses in a circular plan. The circular courses are corbelled near the top to form a dome. Barbed wire is laid between courses to prevent the sandbags from shifting and to provide earthquake resistance. Hence the materials of war – sandbags and barbed wire – are used for peaceful ends, integrating traditional earth architecture with contemporary global safety requirements.
Photos via pushpullbar
The system employs the timeless forms of arches, domes and vaults to create single and double-curvature shell structures that are both strong and aesthetically pleasing. While these load-bearing or compression forms refer to the ancient mudbrick architecture of the Middle East, the use of barbed wire as a tensile element alludes to the portable tensile structures of nomadic cultures. The result is an extremely safe structure. The addition of barbed wire to the compression structures creates earthquake resistance; the aerodynamic form resists hurricanes; the use of sandbags aids flood resistance; and the earth itself provides insulation and fireproofing.
Several design prototypes of domes and vaults were built and tested. The system is particularly suitable for providing temporary shelter because it is cheap and allows buildings to be quickly erected by hand by the occupants themselves with minimum training. The shelters focus on the economic empowerment of people by participation in the creation of their own homes and communities.
Each shelter comprises one major domed space with some ancillary spaces for cooking and sanitary services. Incremental additions such as ovens and animal shelters can also be made to provide a more permanent status and the technology can also be used for both buildings and infrastructure such as roads, kerbs, retaining walls and landscaping elements.
Because the structures use local resources – on-site earth and human hands – they are entirely sustainable. Men and women, old and young, can build since the maximum weight lifted is an earth-filled can to pour into the bags. Barbed wire and sandbags are supplied locally, and the stabilizer is also usually locally sourced.
The prototype is a symbiosis of tradition and technology. It employs vernacular forms, integrating load-bearing and tensile structures, but provides a remarkable degree of strength and durability for this type of construction, which is traditionally weak and fragile, through a composite system of sandbags and barbed wire. Created by packing local earth into bags, which are then stacked vertically, the structures are not external systems applied to a territory, but instead grow out of their context, recycling available resources for the provision of housing. The sustainability of this approach is further strengthened because the construction of the sandbag shelters does not require external intervention but can be built by the occupants themselves with minimal training. The system is also highly flexible: the scale of structures and arrangement of clusters can be varied and applied to different ecosystems to produce settlements that are suitable for different numbers of individuals or groups with differing social needs. Due to their strength, the shelters can also be made into permanent housing, transforming the outcome of natural disasters into new opportunities.